虽说 Google Fonts 所用域名 fonts.googleapis.com 在中国大陆有节点,但墙内各运营商不同的政策导致可能在部分地区无法访问或间歇无法访问,这会导致可能部分地区用户无法加载字体。
目前虽说有很多有心人搭设了 Fonts 反代服务,但不能保证稳定性,自建才是最稳妥的方案。
而使用 Cloudflare Worker 搭设 Google Fonts 反代十分简单,还不用额外的 VPS,推荐使用:
部署
登入 Cloudflare,进入 Worker 界面,点击新建 Worker
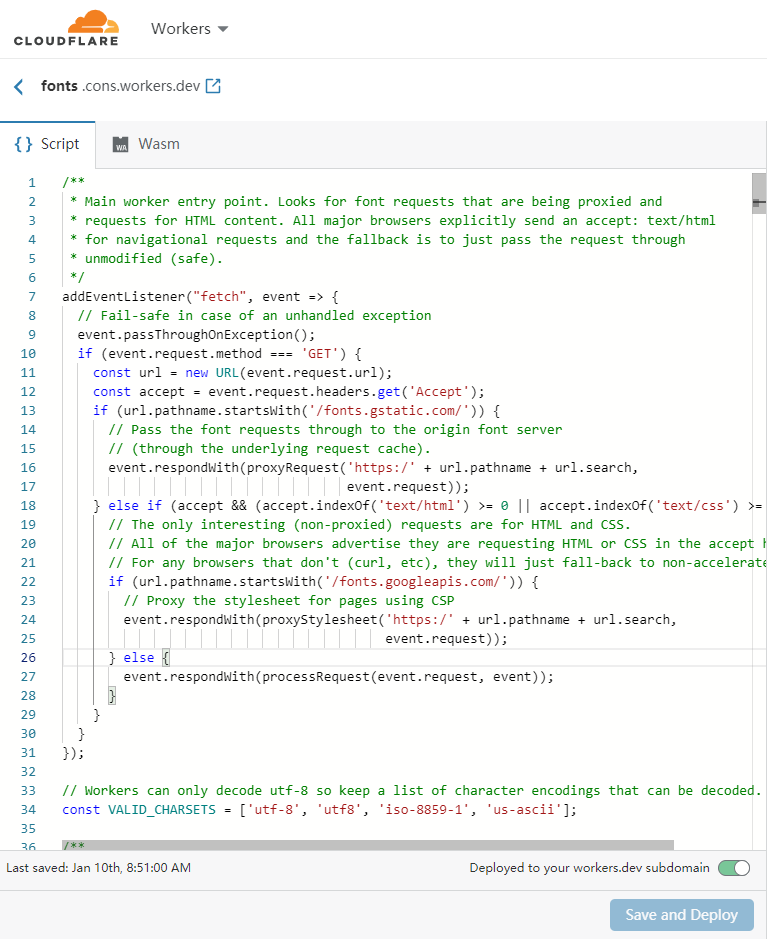
复制以下代码:
addEventListener("fetch", event => {
// Fail-safe in case of an unhandled exception
event.passThroughOnException();
if (event.request.method === 'GET') {
const url = new URL(event.request.url);
const accept = event.request.headers.get('Accept');
if (url.pathname.startsWith('/fonts.gstatic.com/')) {
// Pass the font requests through to the origin font server
// (through the underlying request cache).
event.respondWith(proxyRequest('https:/' + url.pathname + url.search,
event.request));
} else if (accept && (accept.indexOf('text/html') >= 0 || accept.indexOf('text/css') >= 0)) {
// The only interesting (non-proxied) requests are for HTML and CSS.
// All of the major browsers advertise they are requesting HTML or CSS in the accept header.
// For any browsers that don't (curl, etc), they will just fall-back to non-accelerated.
if (url.pathname.startsWith('/fonts.googleapis.com/')) {
// Proxy the stylesheet for pages using CSP
event.respondWith(proxyStylesheet('https:/' + url.pathname + url.search,
event.request));
} else {
event.respondWith(processRequest(event.request, event));
}
}
}
});
// Workers can only decode utf-8 so keep a list of character encodings that can be decoded.
const VALID_CHARSETS = ['utf-8', 'utf8', 'iso-8859-1', 'us-ascii'];
async function proxyRequest(url, request) {
let init = {
method: request.method,
headers: {}
};
// Only pass through a subset of headers
const proxyHeaders = ["Accept",
"Accept-Encoding",
"Accept-Language",
"Referer",
"User-Agent"];
for (let name of proxyHeaders) {
let value = request.headers.get(name);
if (value) {
init.headers[name] = value;
}
}
// Add an X-Forwarded-For with the client IP
const clientAddr = request.headers.get('cf-connecting-ip');
if (clientAddr) {
init.headers['X-Forwarded-For'] = clientAddr;
}
const response = await fetch(url, init);
if (response) {
const responseHeaders = ["Content-Type",
"Cache-Control",
"Expires",
"Accept-Ranges",
"Date",
"Last-Modified",
"ETag"];
// Only include a strict subset of response headers
let responseInit = {status: response.status,
statusText: response.statusText,
headers: {}};
for (let name of responseHeaders) {
let value = response.headers.get(name);
if (value) {
responseInit.headers[name] = value;
}
}
// Add some security headers to make sure there isn't scriptable content
// being proxied.
responseInit.headers['X-Content-Type-Options'] = "nosniff";
const newResponse = new Response(response.body, responseInit);
return newResponse;
}
return response;
}
async function proxyStylesheet(url, request) {
let css = await fetchCSS(url, request)
if (css) {
const responseInit = {headers: {
"Content-Type": "text/css; charset=utf-8",
"Cache-Control": "private, max-age=86400, stale-while-revalidate=604800"
}};
const newResponse = new Response(css, responseInit);
return newResponse;
} else {
// Do a straight-through proxy as fallback
return proxyRequest(url, request);
}
}
async function processRequest(request, event) {
const response = await fetch(request);
if (response && response.status === 200) {
const contentType = response.headers.get("content-type");
if (contentType && contentType.indexOf("text/html") !== -1) {
return await processHtmlResponse(response, event.request, event);
} else if (contentType && contentType.indexOf("text/css") !== -1) {
return await processStylesheetResponse(response, event.request, event);
}
}
return response;
}
async function processHtmlResponse(response, request, event) {
const contentType = response.headers.get("content-type");
const charsetRegex = /charset\s*=\s*([^\s;]+)/mgi;
const match = charsetRegex.exec(contentType);
if (match !== null) {
let charset = match[1].toLowerCase();
if (!VALID_CHARSETS.includes(charset)) {
return response;
}
}
let embedStylesheet = true;
let csp = response.headers.get("Content-Security-Policy");
if (csp) {
// Get the style policy that will be applied to the document
let ok = false;
let cspRule = null;
const styleRegex = /style-src[^;]*/gmi;
let match = styleRegex.exec(csp);
if (match !== null) {
cspRule = match[0];
} else {
const defaultRegex = /default-src[^;]*/gmi;
let match = defaultRegex.exec(csp);
if (match !== null) {
cspRule = match[0];
}
}
if (cspRule !== null) {
if (cspRule.indexOf("'unsafe-inline'") >= 0) {
ok = true;
embedStylesheet = true;
} else if (cspRule.indexOf("'self'") >= 0) {
ok = true;
embedStylesheet = false;
}
}
// If CSP is enabled but there are no style rules, just bail
// (shouldn't work even normally but no reason to touch it).
if (!ok) {
return response;
}
}
// Create an identity TransformStream (a.k.a. a pipe).
// The readable side will become our new response body.
const { readable, writable } = new TransformStream();
// Create a cloned response with our modified stream
const newResponse = new Response(readable, response);
// Start the async processing of the response stream
modifyHtmlStream(response.body, writable, request, event, embedStylesheet);
// Return the in-process response so it can be streamed.
return newResponse;
}
async function processStylesheetResponse(response, request, event) {
let body = response.body;
try {
body = await response.text();
const fontCSSRegex = /@import\s*(url\s*)?[\('"\s]+((https?:)?\/\/fonts.googleapis.com\/css[^'"\)]+)[\s'"\)]+\s*;/mgi;
let match = fontCSSRegex.exec(body);
while (match !== null) {
const matchString = match[0];
const fontCSS = await fetchCSS(match[2], request, event);
if (fontCSS.length) {
body = body.split(matchString).join(fontCSS);
fontCSSRegex.lastIndex -= matchString.length - fontCSS.length;
}
match = fontCSSRegex.exec(body);
}
} catch (e) {
// Ignore the exception, the original body will be passed through.
}
// Return a cloned response with the (possibly modified) body.
// We can't just return the original response since we already
// consumed the body.
const newResponse = new Response(body, response);
return newResponse;
}
function chunkContainsInvalidCharset(chunk) {
let invalid = false;
// meta charset
const charsetRegex = /<\s*meta[^>]+charset\s*=\s*['"]([^'"]*)['"][^>]*>/mgi;
const charsetMatch = charsetRegex.exec(chunk);
if (charsetMatch) {
const docCharset = charsetMatch[1].toLowerCase();
if (!VALID_CHARSETS.includes(docCharset)) {
invalid = true;
}
}
// content-type
const contentTypeRegex = /<\s*meta[^>]+http-equiv\s*=\s*['"]\s*content-type[^>]*>/mgi;
const contentTypeMatch = contentTypeRegex.exec(chunk);
if (contentTypeMatch) {
const metaTag = contentTypeMatch[0];
const metaRegex = /charset\s*=\s*([^\s"]*)/mgi;
const metaMatch = metaRegex.exec(metaTag);
if (metaMatch) {
const charset = metaMatch[1].toLowerCase();
if (!VALID_CHARSETS.includes(charset)) {
invalid = true;
}
}
}
return invalid;
}
async function modifyHtmlStream(readable, writable, request, event, embedStylesheet) {
const reader = readable.getReader();
const writer = writable.getWriter();
const encoder = new TextEncoder();
let decoder = new TextDecoder("utf-8", {fatal: true});
let firstChunk = true;
let unsupportedCharset = false;
let partial = '';
let content = '';
try {
for(;;) {
const { done, value } = await reader.read();
if (done) {
if (partial.length) {
partial = await modifyHtmlChunk(partial, request, event, embedStylesheet);
await writer.write(encoder.encode(partial));
partial = '';
}
break;
}
let chunk = null;
if (unsupportedCharset) {
// Pass the data straight through
await writer.write(value);
continue;
} else {
try {
chunk = decoder.decode(value, {stream:true});
} catch (e) {
// Decoding failed, switch to passthrough
unsupportedCharset = true;
if (partial.length) {
await writer.write(encoder.encode(partial));
partial = '';
}
await writer.write(value);
continue;
}
}
try {
// Look inside of the first chunk for a HTML charset or content-type meta tag.
if (firstChunk) {
firstChunk = false;
if (chunkContainsInvalidCharset(chunk)) {
// switch to passthrough
unsupportedCharset = true;
if (partial.length) {
await writer.write(encoder.encode(partial));
partial = '';
}
await writer.write(value);
continue;
}
}
// TODO: Optimize this so we aren't continuously adding strings together
content = partial + chunk;
partial = '';
// See if there is an unclosed link tag at the end (and if so, carve it out
// to complete when the remainder comes in).
// This isn't perfect (case sensitive and doesn't allow whitespace in the tag)
// but it is good enough for our purpose and much faster than a regex.
const linkPos = content.lastIndexOf('<link');
if (linkPos >= 0) {
const linkClose = content.indexOf('/>', linkPos);
if (linkClose === -1) {
partial = content.slice(linkPos);
content = content.slice(0, linkPos);
}
}
if (content.length) {
content = await modifyHtmlChunk(content, request, event, embedStylesheet);
}
} catch (e) {
// Ignore the exception
}
if (content.length) {
await writer.write(encoder.encode(content));
content = '';
}
}
} catch(e) {
// Ignore the exception
}
try {
await writer.close();
} catch(e) {
// Ignore the exception
}
}
async function modifyHtmlChunk(content, request, event, embedStylesheet) {
// Fully tokenizing and parsing the HTML is expensive. This regex is much faster and should be reasonably safe.
// It looks for Stylesheet links for the Google fonts css and extracts the URL as match #1. It shouldn't match
// in-text content because the < > brackets would be escaped in the HTML. There is some potential risk of
// matching it in an inline script (unlikely but possible).
const fontCSSRegex = /<link\s+[^>]*href\s*=\s*['"]((https?:)?\/\/fonts.googleapis.com\/css[^'"]+)[^>]*>/mgi;
let match = fontCSSRegex.exec(content);
while (match !== null) {
const matchString = match[0];
if (matchString.indexOf('stylesheet') >= 0) {
if (embedStylesheet) {
const fontCSS = await fetchCSS(match[1], request, event);
if (fontCSS.length) {
// See if there is a media type on the link tag
let mediaStr = '';
const mediaMatch = matchString.match(/media\s*=\s*['"][^'"]*['"]/mig);
if (mediaMatch) {
mediaStr = ' ' + mediaMatch[0];
}
// Replace the actual css
let cssString = "<style" + mediaStr + ">\n";
cssString += fontCSS;
cssString += "\n</style>\n";
content = content.split(matchString).join(cssString);
fontCSSRegex.lastIndex -= matchString.length - cssString.length;
}
} else {
// Rewrite the URL to proxy it through the origin
let originalUrl = match[1];
let startPos = originalUrl.indexOf('/fonts.googleapis.com');
let newUrl = originalUrl.substr(startPos);
let newString = matchString.split(originalUrl).join(newUrl);
content = content.split(matchString).join(newString);
fontCSSRegex.lastIndex -= matchString.length - newString.length;
}
match = fontCSSRegex.exec(content);
}
}
return content;
}
var FONT_CACHE = {};
async function fetchCSS(url, request) {
let fontCSS = "";
if (url.startsWith('/'))
url = 'https:' + url;
const userAgent = request.headers.get('user-agent');
const clientAddr = request.headers.get('cf-connecting-ip');
const browser = getCacheKey(userAgent);
const cacheKey = browser ? url + '&' + browser : url;
const cacheKeyRequest = new Request(cacheKey);
let cache = null;
let foundInCache = false;
if (cacheKey in FONT_CACHE) {
// hit in the memory cache
fontCSS = FONT_CACHE[cacheKey];
foundInCache = true;
} else {
// Try pulling it from the cache API (wrap it in case it's not implemented)
try {
cache = caches.default;
let response = await cache.match(cacheKeyRequest);
if (response) {
fontCSS = await response.text();
foundInCache = true;
}
} catch(e) {
// Ignore the exception
}
}
if (!foundInCache) {
let headers = {'Referer': request.url};
if (browser) {
headers['User-Agent'] = userAgent;
} else {
headers['User-Agent'] = "Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 8.0; Windows NT 6.0; Trident/4.0)";
}
if (clientAddr) {
headers['X-Forwarded-For'] = clientAddr;
}
try {
const response = await fetch(url, {headers: headers});
if (response && response.status === 200) {
fontCSS = await response.text();
// Rewrite all of the font URLs to come through the worker
fontCSS = fontCSS.replace(/(https?:)?\/\/fonts\.gstatic\.com\//mgi, '/fonts.gstatic.com/');
// Add the css info to the font caches
FONT_CACHE[cacheKey] = fontCSS;
try {
if (cache) {
const cacheResponse = new Response(fontCSS, {ttl: 86400});
event.waitUntil(cache.put(cacheKeyRequest, cacheResponse));
}
} catch(e) {
// Ignore the exception
}
}
} catch(e) {
// Ignore the exception
}
}
return fontCSS;
}
function getCacheKey(userAgent) {
let os = '';
const osRegex = /^[^(]*\(\s*(\w+)/mgi;
let match = osRegex.exec(userAgent);
if (match) {
os = match[1];
}
let mobile = '';
if (userAgent.match(/Mobile/mgi)) {
mobile = 'Mobile';
}
// Detect Edge first since it includes Chrome and Safari
const edgeRegex = /\s+Edge\/(\d+)/mgi;
match = edgeRegex.exec(userAgent);
if (match) {
return 'Edge' + match[1] + os + mobile;
}
// Detect Chrome next (and browsers using the Chrome UA/engine)
const chromeRegex = /\s+Chrome\/(\d+)/mgi;
match = chromeRegex.exec(userAgent);
if (match) {
return 'Chrome' + match[1] + os + mobile;
}
// Detect Safari and Webview next
const webkitRegex = /\s+AppleWebKit\/(\d+)/mgi;
match = webkitRegex.exec(userAgent.match);
if (match) {
return 'WebKit' + match[1] + os + mobile;
}
// Detect Firefox
const firefoxRegex = /\s+Firefox\/(\d+)/mgi;
match = firefoxRegex.exec(userAgent);
if (match) {
return 'Firefox' + match[1] + os + mobile;
}
return null;
}
点击 Save and Deploy 即部署完毕。
使用
在 fonts.googleapis.com 前加上 Worker域名即可,例如:
- 原链接为: https://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Unica+One&display=swap
- 修改后的链接为: https://fonts.cons.workers.dev/fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Unica+One&display=swap
建议绑定自已的域名以防以后 workers.dev 域名被封锁。
您也可以使用博主提供的反代:
- 将
fonts.googleapis.com替换为use.sevencdn.com - 例如 https://use.sevencdn.com/css?family=Unica+One&display=swap
- 不保证稳定性